The Emerging Intersection of AI, IoT, and Satellite Networks: A Weak Signal Reshaping Connectivity
In the convergence of artificial intelligence (AI), the internet of things (IoT), and satellite internet lies a subtle but potentially transformative signal. Advances in AI-enabled IoT devices combined with shifts in satellite constellation orbits and the rollout of next-generation wireless networks could drive a new paradigm of globally connected, intelligent systems. This development might provoke profound disruption across industries reliant on data analytics, remote sensing, and real-time communication, particularly in underserved or remote regions. Understanding this evolving nexus can aid decision-makers in anticipating unknown unknowns and shaping strategic responses.
What’s Changing?
The number of IoT-connected devices is projected to rise sharply, increasing from 16.6 billion in 2023 to potentially 40 billion by 2030 (IoTInsider, Zeeve). A substantial share—up to 75%—of these devices could embed AI capabilities by 2026, enabling them to analyze data autonomously, generate predictive insights, and make decisions without human intervention (Zealousys). This extends IoT from simple sensor networks to intelligent ecosystems capable of adaptive behaviors and self-optimization.
Meanwhile, the satellite internet sector is undergoing critical technical shifts. SpaceX has announced plans to lower its constellation of approximately 4,400 Starlink satellites to around 480 kilometers by 2026 (WebProNews). This altitude reduction could reduce signal latency significantly, making satellite broadband more competitive with terrestrial fiber infrastructure. Lower latency may enhance applications requiring real-time connectivity, such as telemedicine, remote operations, and immersive experiences.
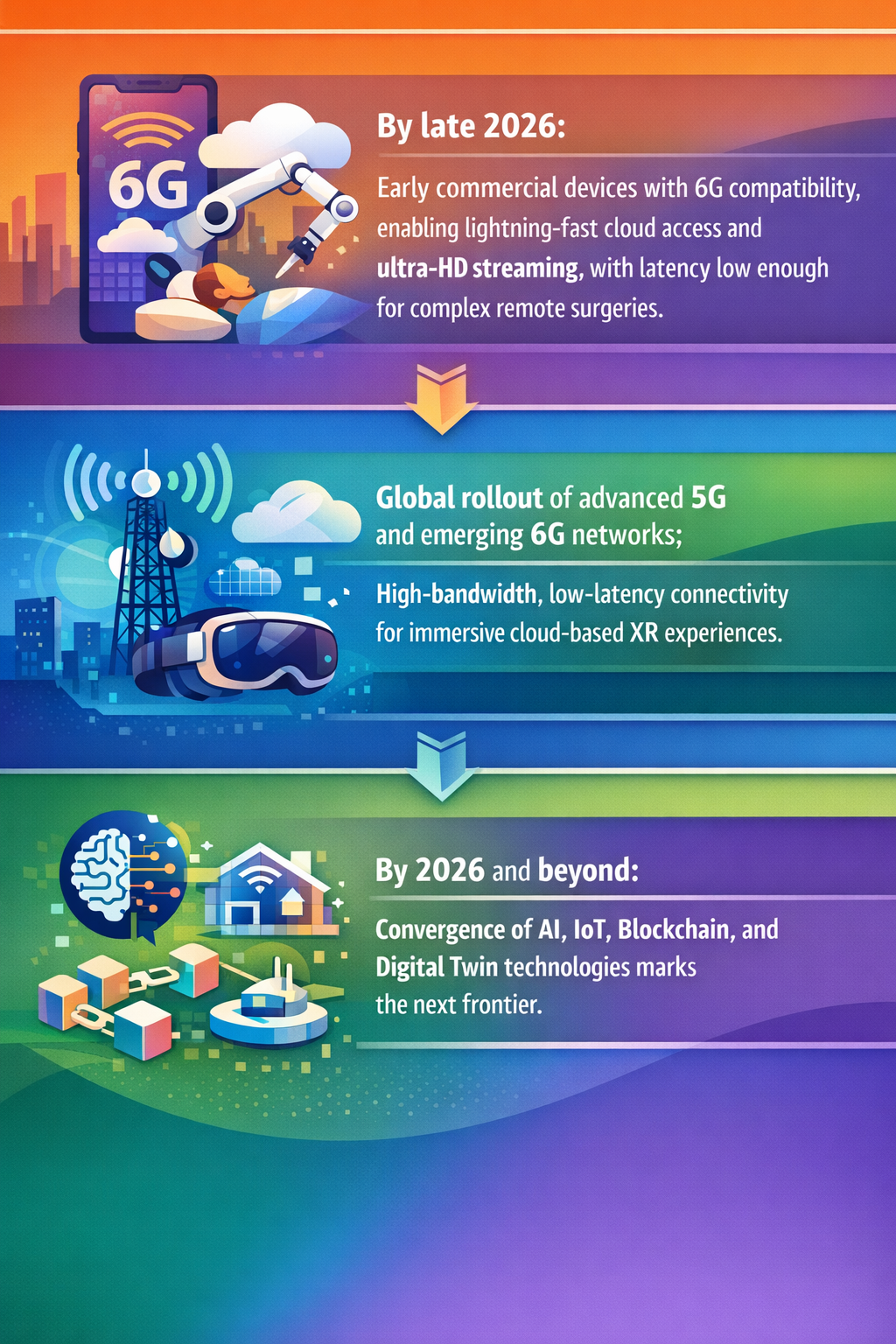
Additionally, the imminent global rollout of advanced 5G networks and the nascent emergence of 6G technologies promise ultra-high bandwidth and ultra-low latency (GoodStrat, inAirspace). These networks could support a new class of cloud-based extended reality (XR) applications, remote surgeries, and other bandwidth-intensive tasks alongside IoT device interconnectivity.
Industry experts are also forecasting a convergence of AI, blockchain, IoT, and digital twin technologies by 2026, highlighting a trajectory toward integrated, resilient, and intelligent systems (STATtimes). Blockchain may support scalable security and automated authentication essential to managing authentication and data exchange for billions of connected devices (Zeeve).
These developments together paint an emerging picture: a globally distributed digital nervous system of AI-enabled, tightly connected IoT devices supported by high-performance low-earth-orbit (LEO) satellite internet and next-generation mobile networks. This could unlock new forms of remote connectivity and data-driven insight in areas and sectors previously unreachable or underserved.
Why Is This Important?
This confluence could reshape multiple industries by enabling critical applications in domains such as:
- Remote healthcare: Lower satellite latency combined with intelligent IoT sensors might enable more effective telehealth, continuous monitoring, and complex remote interventions in rural or disconnected regions.
- Supply chain and logistics: Real-time tracking and AI analytics powered by massive IoT deployments could enhance visibility and predictive maintenance, reducing costs and disruptions.
- Environmental monitoring: Integrated AI-IoT satellite systems could improve detection of weak signals related to climate change and natural disasters over vast geographies.
- Industrial operations: AI-driven IoT devices enabled by ubiquitous, high-speed connectivity might automate fault detection, optimize machine performance, and reduce human error.
Moreover, broadening high-speed connectivity through satellite internet and 6G could democratize digital access, bridging socio-economic divides and fostering innovation hubs in less connected regions. The expected growth of device numbers, combined with automated system management supported by blockchain, introduces questions around scale, security, and data privacy that industries and regulators must address.
Implications
The integration of AI, IoT, and satellite network advancements presents a complex set of strategic implications:
- Infrastructure investment: Organizations may need to rethink infrastructure strategies, balancing terrestrial networks with emerging LEO satellite options to optimize latency-sensitive applications.
- Cybersecurity and trust: The massive scale of interconnected devices necessitates new security paradigms, including decentralized authentication using blockchain to ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized access.
- Regulatory frameworks: Evolving data protection laws must reflect the new realities of pervasive AI-driven data collection and global satellite connectivity, requiring cross-border collaboration.
- Workforce and skillsets: The management of intelligent IoT ecosystems leveraging AI and sophisticated communication networks will demand new expertise in AI operations, satellite communications, and network integration.
- Business model innovation: New service models could emerge based on real-time data analytics, predictive services, and AI-driven automation delivered via satellite-enhanced IoT platforms.
Strategic planners should closely monitor progress in AI-enabled device integration, satellite constellation management, and 6G deployment while preparing for the interoperability challenges and ethical considerations this ecosystem may introduce. The combination of scalability challenges with the promise of enhanced connectivity is a potential source of both opportunity and risk.
Questions
- How might organizations redesign data architectures to accommodate real-time, AI-driven IoT data streams over satellite and 6G networks?
- What frameworks could ensure cybersecurity and ethical data use at the scale of tens of billions of connected devices?
- Which industries stand to be disrupted or radically transformed by highly responsive, satellite-enabled IoT systems?
- How can governments and businesses collaborate internationally to harmonize regulations governing satellite communications and data sovereignty?
- What investments in talent and technology infrastructure are required now to leverage next-generation integrated AI-IoT networks effectively?
Keywords
Artificial Intelligence; Internet of Things; Satellite Internet; 5G Networks; 6G Networks; Low Earth Orbit Satellites; Blockchain; Telemedicine; Extended Reality
Bibliography
- AI-driven IoT applications will surge, with an estimated 75% of IoT devices incorporating AI capabilities by 2026, empowering intelligent data analysis, predictive insights, and autonomous decision-making. Zealousys
- Lower orbits could enable faster data transmission due to reduced latency, benefiting users in remote areas who rely on Starlink for high-speed internet. WebProNews
- The number of connected devices worldwide is expected to reach 21.9 billion in 2026, rising to about 30 billion by the start of the next decade, underscoring the growing centrality of the internet of things to the global economy. IoTInsider
- IoT Explosion: Connected devices will grow from 16.6 billion (2023) to 40 billion by 2030, requiring secure, automated authentication and data exchange at scales traditional systems cannot support. Zeeve
- Satellite internet becoming mainstream will expand connectivity and reshape demand patterns across APAC. Frontier Enterprise
- The road ahead - Integrated, resilient, intelligent Looking toward 2026 and beyond, industry leaders see a convergence of AI, IoT, blockchain, and digital twin technologies as the next frontier. STATtimes
- The global rollout of advanced 5G and nascent 6G networks will provide the high-bandwidth, low-latency connectivity required for truly immersive cloud-based XR experiences. inAirspace
- TechTimes on the foldable future By late 2026, expect early commercial devices to feature 6G compatibility, offering users lightning-fast cloud access, ultra-HD streaming, and latency low enough to support complex remote surgeries. GoodStrat